The 1-Page Marketing Plan by Allan Dib | Summary
Are you a small business owner looking for some practical advice to help market your products or services? Do you need an easy-to-implement plan that won’t take up too much of your time or resources?
If so, The 1-Page Marketing Plan by Allan Dib shows you how to create fast and straightforward marketing and sales systems!
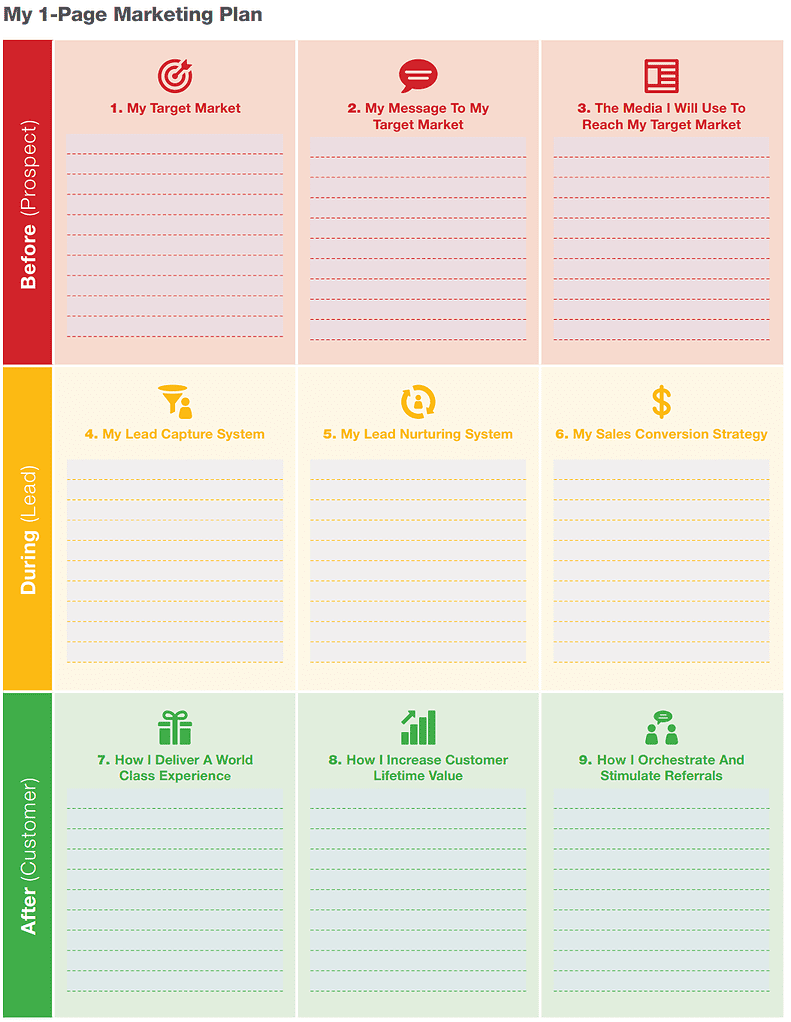
It is easy to see why it is one of the best marketing books due to its simplicity. The book presents a single page broken up into nine squares, with each chapter discussing the respective square.
In this blog post, we will provide a “The 1-Page Marketing Plan” summary and highlight the key ideas from each chapter. By following the principles outlined in this blog pose, you can take full advantage of today’s marketing landscape and ensure that your business is ready to achieve marketing success long into the future.
Buy The 1-Page Marketing Plan on Amazon

The 1-Page Marketing Plan by Allan Dib
Get New Customers, Make More Money, And Stand Out From The Crowd
Download The PDF Book Summary For The 1-Page Marketing Plan
Introduction
Dib summarizes marketing as the “fastest path to the money.” If you didn’t go into business to make money, then you are lying or have a hobby. Many business owners struggle as they turn their hobby or skill into a business without any business skills. Instead, professionals never wing it and follow plans to improve their chances of succeeding.
Dib recommends using the Marketing Plan over a Business Plan to be successful and bases his plan on the following:
- Pareto Principle – states 20% of the marketing causes will result in 80% of the revenue and sales
- Leverage – the idea that successful business owners will spend their personal resources of money to save time
Thus, the 1-Page Marketing Plan will be the most significant leverage point in any business. Using the Double Pareto principle, Dib believes that his practical, simple-to-use document will require 4% of the marketing effort to generate 60% of your business results.
Source: 1-Page Marketing Plan
Dib provides a blank 1PMP canvas you can use for creating your own personal 1-Page Marketing Plan. You should print it out and eat that frog of filling it in as you read the book or this summary.
The “Before” Phase
In the Before Phase of The 1-Page Marketing Plan, the goal is to get the prospect to know you and indicate interest. Prospects are the people that may not know that you or your company exists.
Chapter 1 – Selecting Your Target Market

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
First, you need to select the right target market, so your marketing strategy will be more useful for the number of personal resources invested. You should avoid trying to target everyone or offering an extensive list of products and services.
Focus On A Niche Market
Instead, you should narrow in on a market segment or niche:
Niche – a specialized ideal target market for a particular kind of product or service that helps you:
- Allocate your limited money and become more relevant to prospects
- Allow you to dominate a category or geography
- Establish yourself as a specialist, so you can set your own prices
Target Using The PVP Index
The PVP Index helps you rate your ideal target market from a scale of 1 to 10:
- Personal Fulfillment (P): How much do you enjoy working in this niche with this customer type?
- Value to the Marketplace (V): How much are your customers willing to pay for your work?
- Profitability (P): How profitable is your work in this niche?
Create An Avatar
Additionally, you can dive into the mind your prospect by creating a custom avatar:
Avatar – a detailed expiration and description of your target customer and their lives that will help you get into their mind, understand their wants, and tailor your marketing to them
Fill-in Square 1 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: Who is your Target Market?
Chapter 2 – Crafting Your Message

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
Next, you should craft a compelling message to get your target market’s attention and impel them to respond. Most advertising is bland and ineffective. Instead, your marketing strategy should have purpose with your advertising composed of two critical components:
- Purpose: What is the purpose of your advertising media?
- Focus: What does your advertising media focus on?
Each ad should have one clear objective to communicate to your prospect. Instead of selling right away, provide an easy call to action to show interest. Your message can be crafted in the various formats discussed below. To learn more about turning your message into a compelling story, check out the book, Building a StoryBrand (book summary).
Develop A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Amplify your marketing strategy by developing a USP:
Unique Selling Proposition (USP) – the reason why your business exists, why someone should buy, and why some should choose you over your nearest competitor; has the following characteristics:
- Provide uniqueness that positions you differently
- Attract prospects before they have made a buying decision
- Avoid positioning yourself as a commodity and competing solely on price
- Avoid confusing prospects, as you will lose them
Create An Elevator Pitch
When asked the “what do you do?” question, you can respond with a version of your USP compiled into an elevator pitch:
Elevator Pitch – a concise, rehearsed summary of your business and its value proposition, which:
- Can be delivered in about 30-90 seconds or the time it takes to ride an elevator
- Focuses on the solution and the customer instead of the product and oneself
- Takes the prospect on a journey consisting of the problem, resolution, and proof: You know [problem]? Well, what we do is [solution]. In fact [proof].
Craft An Amazing Offer
Before creating a unique, exciting offer, you need to ask yourself, of all your offerings:
- Which can you most confidently deliver?
- Which do you enjoy delivering the most?
When it comes to buying decisions, the offer should be done with emotions and justified with logic afterward:
Offer – the product or service you are selling, which can include the following elements:
- Value – the problem that you will solve for your customer
- Language – the words and jargon used by your target market
- Reason Why – the justification why you are doing this
- Value Stacking – the bonuses to help increase conversions
- Upsells – the complementary offerings to add value and increase profits
- Payment Plan – the division of an outstanding balance over time to increase sales
- Guarantee – the promise to your customer to take on the risk if you fail to deliver
- Scarcity – the fear of loss that gets your prospects to respond and buy immediately
For more on creating irresistible offers, check out The Irresistible Offer (book summary) or $100M Offers (book summary).
Sell Through Copywriting
Next, you can master emotional direct response copywriting:
Copywriting – the skill of writing compelling words that convince prospects to take action and buy your products or services; has the following characteristics:
- Convey opinion, insight, advice, and commentary
- Embody your personality and authenticity to build rapport
- Appeal to the five motivators of human behavior: fear, love, greed, guilt, and pride
- Create headlines that grab the attention of your target market
- Tell prospects who your offer is not for to filter, establish credibility, and induce exclusivity
Name Your Offer Or Business
To effectively name your product, service, or business, follow these rules:
- Title Should Equal Content: The name should clearly indicate the product, service, or business.
- Clarity Over Cleverness: Do not confuse or try to be witty, as you will lose prospects.
Fill-in Square 2 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: What is your Message to your Target Market?
Download The PDF Book Summary For The 1-Page Marketing Plan
Chapter 3 – Reaching Prospects With Advertising Media

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
Advertising media is the vehicle to reach your target market and communicate your message.
Measure Your Marketing Spend
Marketing is expensive, so it can be managed using the following metrics or data points:
- Return on Investment (ROI) – The Return on Investement measures the percentage of profit generated from a marketing campaign, relative to the marketing cost.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The Customer Acquisition Cost measures the total cost of marketing required to gain a customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) – The Customer Lifetime Value measures the total value to a business of a customer over the entire relationship; divided between:
- Front End – the profit made on the initial sale; the goal is to turn prospects into customers
- Back End – the profit made on subsequent sales for the rest of the relationship
Peter Drucker has said, “What gets measured, gets managed,” so avoid spending on branding or “getting your name out there.”
Pick A Marketing Medium
There are many ways to get your compelling message out there, including radio, TV, social media, search engine optimization (SEO), and email marketing. Avoid choosing only one medium for marketing, as this is a “single point of failure.” You should hire experts and buy services specifically for your chosen marketing medium:
Social Media – digital website or application that allows you to:
- Create and share content with the public quickly
- Build credibility, develop relationships, and engage with people
- Drive traffic to site/email list as you don’t own the audience and is not an ideal place to sell
Email Marketing – a direct, personal way to engage with prospects and customers that allows you to:
- Build a list of email subscribers to market and eventually sell to
- Provide value and self-promotion using personalized content and
- Maintain a close relationship with your paying customers, to which you can test and launch new offerings
Snail Mail – the postal mail, which complements email and allows you to:
- Send physical objects to induce emotion; for example, a handwritten card is more powerful than a text
- Send something that lasts longer and requires more effort to dispose of than email
- Stand out as it is much less cluttered than email marketing
Pay For Marketing And Don’t Budget
When you spend money on marketing, one of the following occurs:
- Failure: Your marketing expenses cost more than your sales revenue, so change or stop your marketing efforts.
- Unknown Result: You don’t know whether your marketing was successful, so track and measure your return on investment (ROI).
- Success: Your sales revenue is greater than your marketing expenses, so put more resources behind it.
Thus, you should avoid setting a marketing budget unless you are testing out different marketing tactics. Remember, paid marketing has two critical benefits:
- Reliability: Has a higher likeliness of being run when paid for.
- Measurability: Focuses you to track return marketing using metrics.
Fill-in Square 3 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: What Media will you use to reach your Target Market?
The “During” Phase
In the During Phase of the 1-Page Marketing Plan, the goal is to get the lead to buy from you for the first time. Leads are the people that know you and have indicated interest to your marketing message.
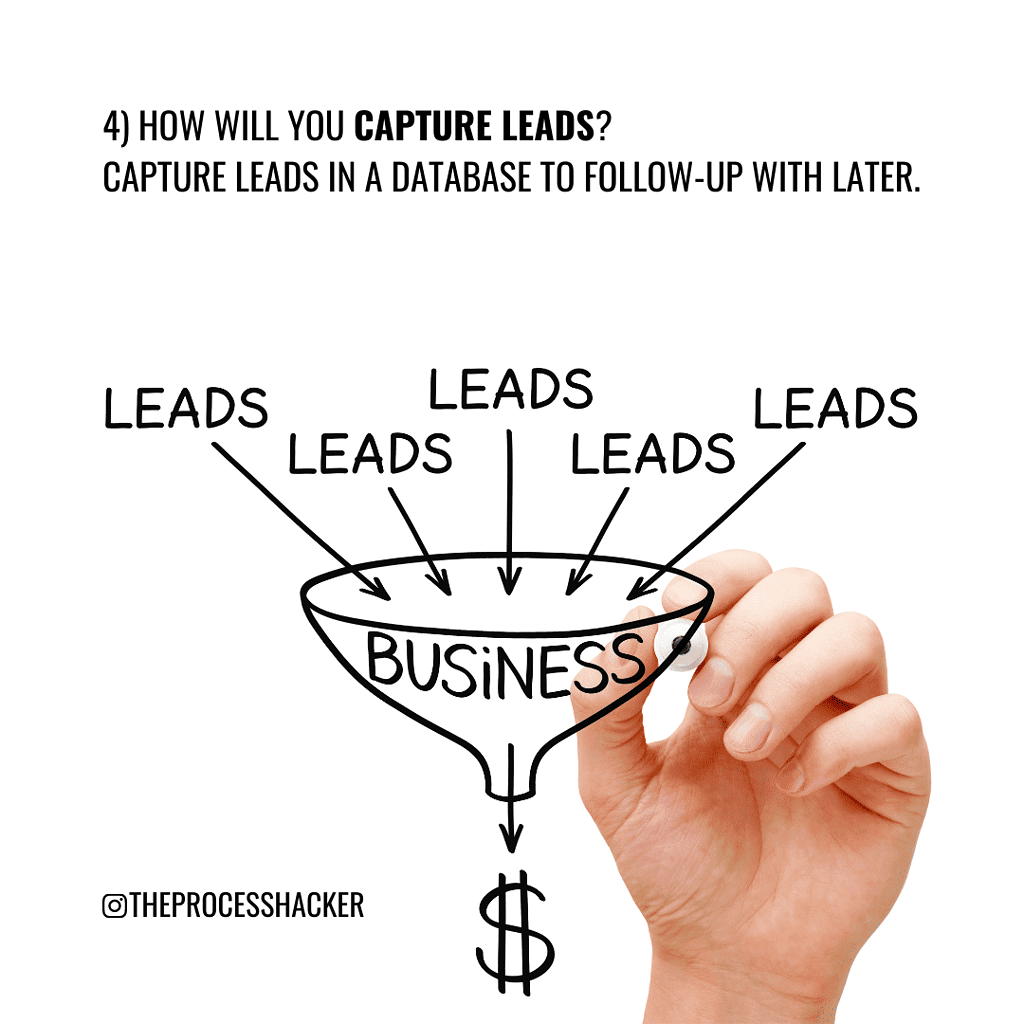
Chapter 4 – Capturing Leads
Instagram: @theprocesshacker
Capturing leads is the marketing process of storing leads in a database system or future sales pipeline follow-up.
Avoid Selling From Your Marketing
Don’t be desperate and sell directly from your advertising, as on average:
- 3% are ready to buy immediately
- 7% are very open to buying
- 30% are interested but not at the moment
- 60% are not interested
As most people will not be ready to buy, use your advertising to generate leads and increase your addressable market to 40%.
Capture Leads In A CRM
Instead, you can correctly handle interest by capturing interested leads using a CRM system:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system – a database that allows you to:
- Store lead information such as name and email
- Build value by providing content and information
- Establish yourself as an expert in your target market
- Foster a relationship built on trust to sell to eventually
Focus On Higher Value Prospects
Don’t treat all prospects equally, as spending more on higher probability prospects will result in more conversations. Offer an “ethical bribe” to help you identify the high probability prospects.
Fill-in Square 4 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: How will you Capture Leads?
Download The PDF Book Summary For The 1-Page Marketing Plan
Chapter 5 – Nurturing Leads

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
The lead nurturing process is the marketing process of guiding people from being vaguely interested in your offerings to wanting to do business with you.
Follow-Up With Leads
The key to building a nurturing marketing campaign is in following-up with your leads as:
- 50% of salespeople give up after one contact
- 65% give up after two contacts
- 80% five up after three contacts
Following up will build a strong relationship with your leads over. Be more compelling and prolific in your offers to gain 10X more leads, make more sales, and grow more rapidly.
Create Your Marketing Infrastructure
Your marketing infrastructure will help your follow-up by interesting, motivating, and qualifying leads by:
- Staying in regular contact, so leads don’t forget about you
- Providing value using tutorials, articles, case studies, or a regular newsletter.
- Occasionally, pitching them your products or services.
Several assets make up your marketing infrastructure, including websites, newsletters, blogs, email sequences, social media, podcasts, hand-written notes, and more.
Each asset has a place and a purpose and should nurture leads. The author recommends using the following methods to provide outsized value and make a powerful impression:
- Lumpy Mail – an oversized piece of postage designed to grab attention
- Shock and Awe Package – a physical box to deliver goods, such as books, gifts, brochures, samples, etc.
Grow Your Marketing Team
You can’t do everything yourself, so you need to delegate properly as a business owner. Thus, your business requires a team of the following three types of people to grow:
- Entrepreneur – the visionary that sees a problem and will solve that problem for profit
- Specialist – the implementer to take the entrepreneur’s vision and make it a reality
- Manager – the doer that gets work done and ensures gaining traction on the vision
In the Entrepreneurial Operating System, these business roles are divided into the Visionary (Entrepreneur) and Implementer (Specialist/Manager). Learn more about each role by reading our summary of Rocket Fuel. Or if you are just starting out as an entrepreneur, check out Entrepreneurial Leap (book summary) by Gino Wickman.
You need to create processes to consistently run your marketing activities:
- Marketing Calendar Activities – the scheduled marketing activities that occur daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, and annually
- Event Triggering Marketing Activities – those marketing actions that occur in response to an event like receiving an email inquiry, gaining a subscriber, or receiving a complaint
For each marketing activity, you need to define the people who are responsible for each action.
Fill-in Square 5 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: How will you Nurture Leads?
Chapter 6 – Sales Conversion

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
Sales conversion is the marketing process of building trust and providing value to motivate leads to buy your products or services.
Position To Make Money
Many people think that a better product or service will automatically cause people to buy from you and pay you more for it. However, the real profit comes from how you position yourself to charge higher prices for your goods and services. You want to be the welcomed guest that is familiar and brings value instead of the pest that bothers you and wants to take.
Manufacture Trust
You need to present your business and offerings in a way that conveys confidence and builds trust. Do not sell directly and instead educate, consult, and advise leads to the benefits of your products and services.
Use the following technology to present your business professionally:
- Website: As this is the first place people learn about your business, make the site attractive. Also, include a phone number, physical business address, and privacy policy.
- Email Address: Use your own domain email instead of one from Hotmail, Gmail, etc.
- Phone Number: Get a national toll-free number or toll-free word number.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System: Manage customer details automatically and adequately.
- Ticketing System: This system can help you keep track of customer requests, inquiries, and support.
Price Strategically
You need to set prices properly to position the product or service and make the sales conversion process easy using the following factors:
- Limit Options: Don’t give too many choices, so instead offer a “standard” version and “premium” version (priced at 50% above the “standard” but offers twice the value).
- Reverse Risk: Provide an “unlimited” version of your product or service for a fixed price.
- Offer an Ultra High-Ticket Item: Since a small percentage want to buy the “best” option, offer a unique, expensive product or service.
- Resist Discounting: Don’t discount, and instead increase the value of your offering by giving bonuses, more products, or extra services.
Remove Roadblocks That Prevent Sales
There are several ways to remove obstacles that are preventing people from buying:
- Provide an Outstanding Guarantee: A guarantee allows you to remove the customer’s perceived risk if the product or service does not work out. Ordinary guarantees like “money-back guarantee” or “satisfaction guaranteed” are not very powerful.
- Have Them “Try Before Buying:” This method will make the lead feel like they are not committing to your offering. A genuine customer is unlikely to return the right product that meets their needs.
- Make Buying Easy: The sales process should be easy and painless by removing lengthy forms, providing multiple ways to pay, and offering payment plans.
Fill-in Square 6 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: What will be your Sales Conversion Strategy?
Download The PDF Book Summary For The 1-Page Marketing Plan
The “After” Phase
In the After Phase of the 1-Page Marketing Plan, the goal is to get the customer to trust you and buy from you regularly and refer. Customers are the people that pay you money for your products or services. This cycle lasts indefinitely and can virtuously result in your customers continually buying your offerings.
Chapter 7 – Delivering A World Class Experience

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
A world-class experience has customers buying from you repeatedly and is implemented using the most valuable business systems.
Build A Tribe Of Raving Fans
To be successful, you need to turn your customers into a “tribe of raving fans:”
Tribe – a group of people connected to one another, connected to a leader, and connected to an idea
Your tribe will want you to succeed and amplify your marketing message. For more on leadership, check out The 5 Levels of Leadership (book summary).
There are several characteristics of businesses that lead tribes:
- Influence your customers to take action to achieve results with your product or service
- Create theatre around their products and services in innovative ways
- Use technology to eliminate friction to provide a fast sale and increase satisfaction
- Provide value, position yourself as an expert, and maintain lifelong relationships
- Educate your audience on the effort required to deliver your product or service
Systematize Your Business
A system will make you successful and help grow your business:
Business System – uses document processes to allow your people to run your business without you
There are four central business systems that will make you successful:
- Marketing – the system that generates a consistent flow of leads into the business
- Sales – the system that nurtures, follow-ups, and converts leads
- Fulfillment – the that provides the product or service in exchange for payment
- Administration – the system that supports business functions and includes accounting, reception, human resources, etc.
Implementing business systems have the following benefits:
- Builds a Valuable Asset to provide cash flow to finance your lifestyle.
- Allows for Leverage and Scalability to serve more customers.
- Provides Consistency of products and services to customers.
- Lower Costs for labor and production as replicating improves efficiency.
- Remove Yourself to eliminate the biggest bottleneck in your business.
The business system is captured in an operations manual, which contains checklists, procedures, and training. There are three steps to capture processes:
- Identify all the positions in your business.
- Define the tasks that each role needs to perform. To learn more about structuring a business and defining roles, read our post on Accountability Charts.
- Document your process using checklists, which create a list of all tasks in a specific process. To learn more about checklists, read our post summarizing the book, The Checklist Manifesto.
Plan For Your Exit
When starting and running a business, you need to plan your exit strategy and sale to your ultimate customer:
Ultimate Customer – the person or company that puts you out of business
You can make a lot of money running a business, but you will make much more selling one. Documented systems will allow you to sell and pass on the company to someone else to run.
Fill-in Square 7 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: How will you deliver a World-Class Experience?
Chapter 8 – Increasing Customer Lifetime Value

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
Increasing lifetime value of those who have already bought from you will result in higher profits.
Make More Profit From Existing Customers
One is 21 times more likely to buy from a business they’ve purchased from in the past than one they’ve never bought from. Thus, your existing customer base is similar to a rich diamond mine that needs to be sold to more and more to realize its real value. There are five primary ways to make more money from existing customers:
Raising Prices – the act of increasing prices over time
- Don’t keep prices fixed as the value will decrease due to inflation
- Provide explanations of price raises to your customers
- Use “grandfathering” to hold prices constant only for existing customer
Upselling – the bundling of add-ons with the primary product or service being sold to provide an additional benefit
- Use the contrast principle as the suggested add-on fells comparatively cheaper
- Buyers are less price-sensitive to the add-on as they weren’t shopping for it
Accession – the process of upgrading existing customers from their current product or service to a more expensive offering:
- Prevent customers from switching to competitor’s product or service
- Don’t provide only one offer as you are leaving money on the table
- Provide your customers with something to aspire to
Frequency – the method of getting customers to buy more often using:
- Reminders: Send snail mail, email, or text to sell again or maintain the relationship
- Reasons to Buy Again: Provide vouchers or coupons, so customers come back
- Reasons to Buy Repeatedly: Use the subscription model to make money automatically
Reactivation – the method of restarting the customer relationship by:
- Search your CRM database for a list of existing and past customers you haven’t heard from
- Make a strong offer to get them to buy again (gift card, coupon, etc.)
- Contact past customers to ask why they haven’t repurchased from you
Manage Your Business Using Key Metrics
Data will help you manage and improve your business. Improving your key metrics by a small amount can have an outsized impact on the bottom line.
Key Marketing Metrics:
- Leads – the number of new leads that you capture
- Conversion Rate – the percentage of leads that you converted into paying customers
- Average Transaction Value – the average amount that leads spend with you
- Break-Even Point – the amount you need to earn in revenue to offset expenses
Key Subscription or Recurring Business Metrics:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue – the total recurring billing from your products or services
- Churn Rate – the percentage of recurring customers that cancel their subscriptions
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) – the total customer value to over the entire relationship
You can use a business dashboard or scorecard to track numbers, identify issues, and motivate your team.
Identify Great Customers And Fire Problem Ones
There are four types of customers in your business:
- Tribe – the raving fans that promote your business, want you to succeed, and provide healthy revenue
- Churners – the customers that can’t afford you that leave and criticize your brand
- Vampires – the customers that can afford you, but you can’t afford them as they overwhelm and are difficult
- Snow Leopard – the rare customer that pays you considerably and is easy to work with
A formal way to categorize customers is using NPS:
Net Promoter Score (NPS) – measures customer loyalty and satisfaction in terms of promoters, detractors, or passives
Thus, all business revenue is not equal as some comes from toxic customers (churners, vampires, or detractors) that provide “polluted revenue.” Therefore, you should fire your problem customers free up your precious resources to focus on your high-value tribe.
Fill-in Square 8 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: How will you increase Customer Lifetime Value?
Download The PDF Book Summary For The 1-Page Marketing Plan
Chapter 9 – Orchestrating And Stimulating Referrals

Instagram: @theprocesshacker
Instead of relying on word of mouth, you should be actively orchestrating and stimulating referrals. Many businesses rely on word of mouth, which puts the fate of other people’s hands.
Ask For Referrals
The “Law of 250” tells us that every person represents about 250 potential referrals, which is the number of important people in one’s life. Thus, you can ask and compel existing customers to give you referrals without seeming desperate using these strategies:
- Acknowledge them and appeal to their ego
- Not asking for a favor, but offering value to someone in their network
- Give them a reason why they should provide referrals
- Create an expectation of proving a specific number of referrals
Profit Through Joint Ventures
Your customers spend money with other businesses, so you can make deals with other companies through JCs:
Joint Venture (JC) – an agreement in which two or more businesses agree to pool their resources to accomplish a goal such as selling more together
These JCs can partner you with complimentary businesses to sell products and services together or become a cheap or free source of leads.
Monetize Your Existing Customer Base
Also, there are several ways to monetize your existing customer base:
- Sell Leads with a complimentary business; however, ensure that you have permission to pass on customer details.
- Exchange Leads with a complimentary business instead of taking payment. Again, ensure that you have customer permission.
- Resell complementary products and services through wholesaling or white labeling and resell these to your customer base. This method ensures that you control your customer details.
- Become an affiliate referral partner, so that you get paid a commission on sales for each referral sent.
Build Your Brand
There are many definitions of a brand with Dib stating the following:
Brand – the personality of a business, which has the following attributes:
- Name and Design: How does it present itself?
- Positioning: How does it communicate?
- Brand Promise: What are its core values? What does it stand for?
- Ideal Target Market: Who does it associate with?
- Brand Awareness: How well-known is it?
Rather than getting someone to buy, branding should be done after a customer has purchased your product or service. Instead, you should create brand equity:
Brand Equity – the goodwill you build up that compels people to do business with you over your competitor
Thus, focus on the sale and then turn your customers into a tribe of raving fans to work on branding.
Fill-in Square 9 of Your 1-Page Marketing Plan: How will you orchestrate and stimulate referrals?
Download The PDF Book Summary For The 1-Page Marketing Plan
Conclusion And Next Steps
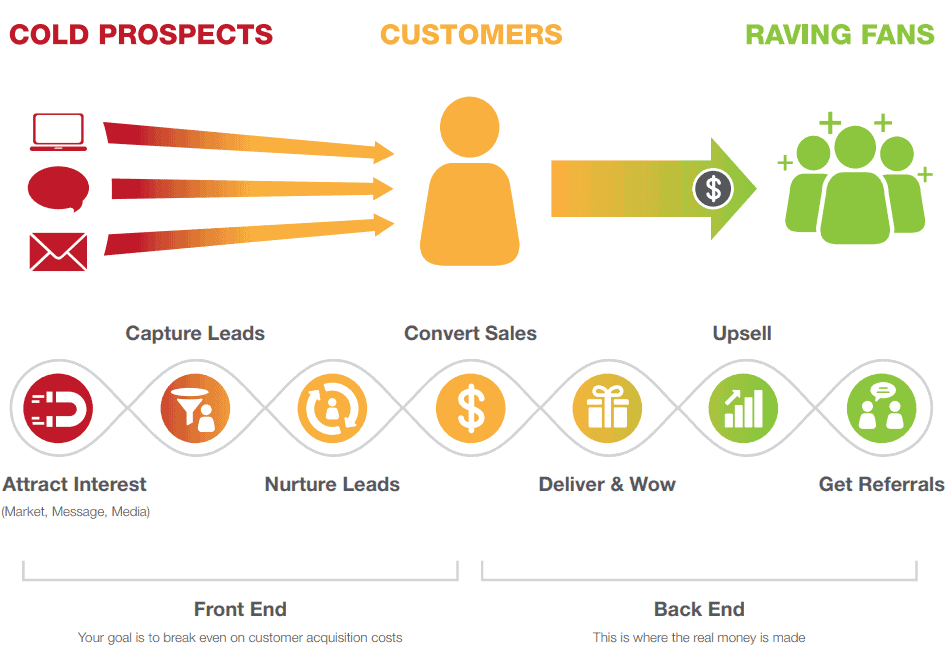
The 1-Page Marketing Plan can be the leverage point in your business to be the “fastest path to the money.” In the Conclusion, Dib provides a big-picture view of the entire marketing process, which is known as the Direct Response Marketing Lifecycle.
You can use the marketing plan to help you get prospects to become interested, get leads to buy your products and services, and turn your customers into raving fans. You will become a successful small business marketer and gain personal fulfillment!
I hope this “The 1-Page Marketing Plan” summary has inspired you to implement the marketing plan and read the book.







