The 3 Critical Financial Statements for Small Business Success
How’s your financial literacy these days? With the demands of running a business, it can be easy to let the numbers slip through the cracks.
But I’m here today with an important reminder: your financial statements are like a crystal ball for your company’s future. Within those magical numerals lies insights into how healthy or unhealthy your business truly is.
Now, I know financials may not exactly get your blood pumping like a Sunday afternoon football game. But trust me when I say neglecting them could spell doom for your dreams of small business success.
That’s why today I’m unveiling the 3 critical financial statements that every entrepreneur needs to understand like the back of their hand. So, let’s jump into a crash course on the financial statements that will keep your business running profitably for years to come!
What are Financial Statements?
Financial statements are essentially dashboards of your business’s financial performance. These documents provide a snapshot of your financial position, operations results, and cash flow over a specific period.
They are indispensable tools for financial reporting. They help you gauge your business’s health and enable you to plan strategically for both short-term operations and long-term growth objectives.
- Balance Sheet: This snapshot of your financial condition at a specific point in time covers your assets, liabilities, and equity. It helps you understand what you own and owe, providing insights into the financial strength and capabilities of your business.
- Income Statement: Sometimes called the profit and loss statement, it outlines your revenues, expenses, and profits over a certain period. This statement is key to tracking profitability and identifying trends in your business operating income and expenditures.
- Cash Flow Statement: This statement breaks down the cash inflows and outflows from operations, investing, and financing activities. It’s crucial to understand how cash moves in and out of your business and assess your company’s liquidity.
Integrating these financial statements into your regular business review process lets you maintain a clear view of your financial trajectory, enabling you to act swiftly and appropriately in response to any financial changes. This proactive approach is vital in maintaining a healthy, sustainable business.
#1) The Balance Sheet: A Snapshot of Financial Position
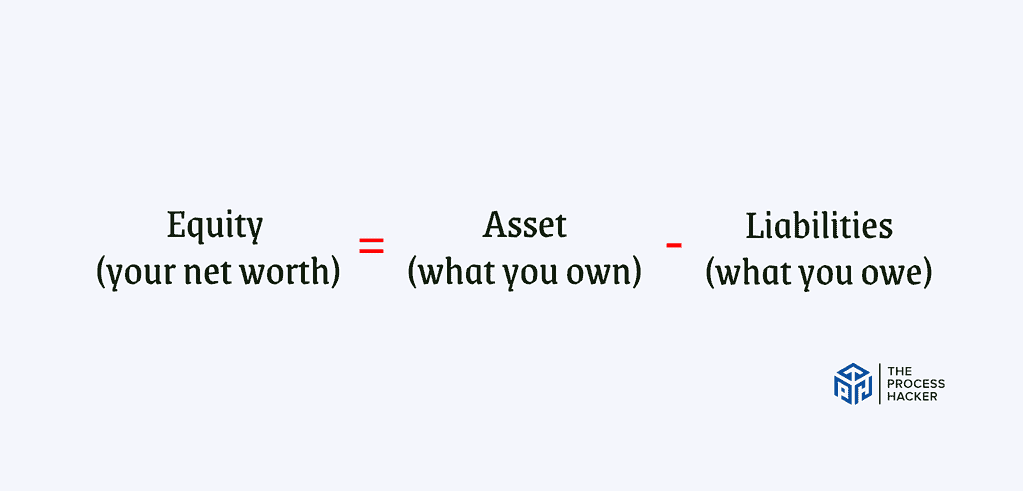
The balance sheet is like a financial photograph – it captures your business’s financial health at a specific moment in time. It’s a simple equation:
Equity (your net worth) = Assets (what you own) ‘ Liabilities (what you owe)
This statement reveals what your business owns (assets), what it owes to others (liabilities), and the remaining value that belongs to you as the owner (equity). It’s essential because it provides a clear picture of your financial strength and stability.
Key Components
Let’s break down the main players on the balance sheet:
- Assets: These are the resources your business owns that have value. They can be tangible (like cash, inventory, equipment) or intangible (like patents, trademarks).
- Liabilities: These are your business’s debts or obligations. They include accounts payable (money you owe to suppliers), loans, and any other outstanding debts.
- Small Business Owners Equity: This is the residual interest in the assets of the business after deducting liabilities. It’s essentially your investment in the business.
How to Use It to Analyze Your Company’s Financial Health
The balance sheet is more than just a list of numbers; it’s a tool for understanding your business’s financial standing. Here’s how you can use it:
- Liquidity: Check your current assets (cash, accounts receivable) against your current liabilities (accounts payable). This tells you if you can meet your short-term obligations.
- Solvency: Compare your total assets to your total liabilities. This reveals your ability to meet long-term obligations and stay afloat.
- Equity: Track changes in your owner’s equity over time. This reflects the growth (or decline) of your investment in the business.
By analyzing these components, you gain valuable insights into your financial health. You’ll see whether you have enough assets to cover your debts, how much you’re worth, and if your business is growing.
#2) The Income Statement: Profitability at a Glance
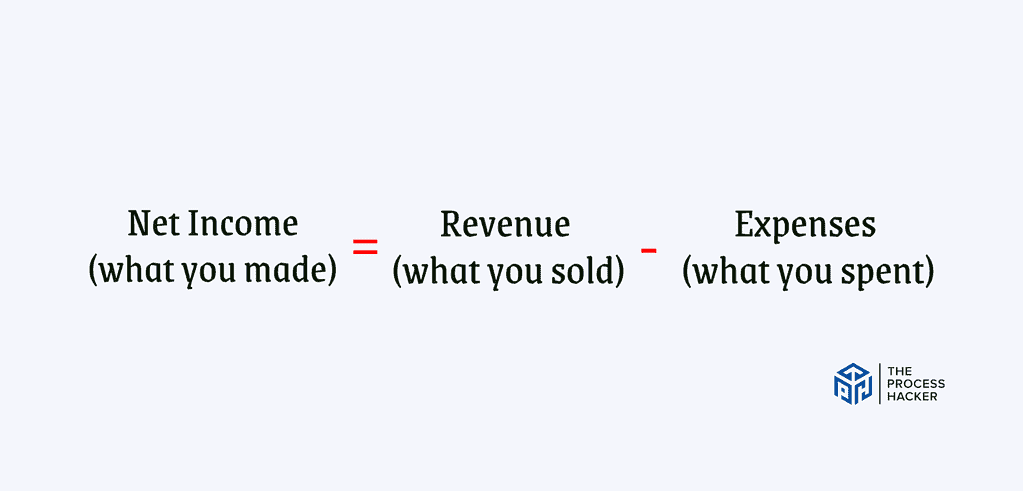
While the balance sheet gives you a snapshot, the income statement tells the story of your business’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. It answers the crucial question: “Is my business making money?”
Net Income (what you made) = Revenue (what you sold) – Expenses (what you spent)
The income statement outlines all the revenue your business generates and subtracts the expenses incurred from retained earnings of that revenue. The result is your net income – the bottom line that shows if you made a profit or loss during that period.
Key Components
The income statement breaks down into these core elements:
- Revenue: This is the total income your business earns from its primary activities, like selling products or services.
- Expenses: These are the costs your business incurs to operate, such as rent, salaries, marketing, and inventory.
- Net Income: This is the final result after subtracting all expenses from revenue. A positive net income means profit, while a negative one indicates a loss.
How to Use It to Analyze Your Profitability
The income statement is a powerful tool for assessing your financial performance. Here’s how you can put it to work:
- Identify Trends: Track your revenue and expenses over time to spot trends. Are sales increasing? Are certain expenses eating into your profits?
- Calculate Profit Margins: Divide your net income by revenue to find your profit margin. This metric shows you how much profit you generate for every dollar of sales.
- Compare Periods: Analyze income statements from different periods (e.g., this year vs. last year) to assess your financial progress. Are you growing? Stagnating? Declining?
By examining these components and trends, you can pinpoint areas for improvement, optimize your pricing, and make strategic decisions that boost your bottom line.
#3) The Cash Flow Statement: Tracking Money Movement
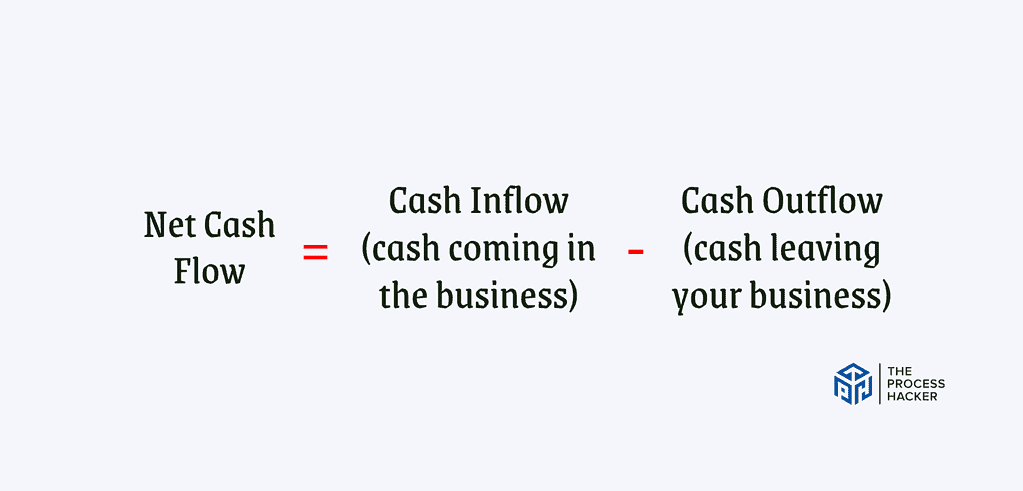
The cash flow statement tracks the flow of cash over a specific period, similar to the income statement. Here is the equation:
Net Cash Flow = Cash Inflow (cash coming in the business) – Cash Outflow (cash leaving the business)
However, it focuses solely on cash transactions, excluding non-cash items like depreciation. This statement is crucial because it reveals your ability to generate cash to pay bills, invest in growth, and ultimately, remain solvent.
Key Sections
The cash flow statement is divided into three main sections, each representing a different source or use of cash:
- Operating Activities: This section shows the cash generated or used in your day-to-day business operations, like sales, purchases, and payments to employees.
- Investing Activities: Here, you’ll see the cash flow related to investments, such as buying or selling assets like equipment or property.
- Financing Activities: This section outlines cash flow from financing activities, including loans, repayments, issuing stock, or paying dividends.
How to Use It for Better Financial Management
Cash flow statements are valuable for managing your finances effectively. Here’s how it can help you:
- Spot Cash Flow Problems: Are you generating enough cash from operations to cover your expenses? If not, the cash flow statements will reveal the shortfall.
- Plan for the Future: By understanding your cash flow patterns, you can better predict future cash needs and make informed decisions about investments, financing, and spending.
- Monitor Financial Health: Changes in your cash flow statement can be early warning signs of financial trouble. By closely monitoring it, you can proactively address issues before they become significant problems.
Think of the cash flow statement as your financial compass, guiding you toward sound decision-making and long-term stability.
How to Prepare Financial Statements
Accurate and timely financial statements are essential for making informed decisions and ensuring your business stays on track. Whether you choose to prepare them yourself or enlist the help of a professional, understanding the process is key.
Gather Financial Data
The first step is to gather all the necessary financial information. This includes:
- Essential Financial Records and Documentation: Bank statements, invoices, receipts, payroll records, loan agreements, and any other documents that detail your income and expenses.
- Using Accounting Software for Accurate Data Collection: Accounting software can significantly streamline this process. It automatically tracks your financial data, categorizes transactions, and generates reports.
- Importance of Maintaining Up-to-Date Financial Information: Keeping your financial records organized and up-to-date is crucial. This not only makes preparing financial statements easier but also helps you stay on top of your finances.
Once you’ve gathered all your financial data, you’re ready to start putting together your financial statements. But remember, accuracy is key! Double-check all your numbers to ensure your statements are reliable.
How to Create Each Financial Statement
With your financial data in hand, it’s time to create the three statements. Don’t worry; it’s not as complex as it might seem.
Building the Balance Sheet:
- List Your Assets: Start by listing all the assets your business owns, categorized as current (convertible to cash within a year) and non-current (held for longer).
- Detail Your Liabilities: Next, list all the debts and obligations your business owes, again categorized as current and non-current.
- Calculate Owner’s Equity: Subtract total liabilities from total assets to arrive at owner’s equity. This represents your net worth in the business.
- Format the Balance Sheet: Organize this information into a standard balance sheet format, ensuring that assets equal liabilities plus equity.
Compiling the Income Statement:
- Calculate Revenue: Add up all the revenue your business earned during the specified period, including sales, services, and other income.
- Total Your Expenses: Sum up all the costs incurred to generate that revenue, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and marketing.
- Determine Net Income: Subtract total expenses from total revenue to find your net income (profit or loss).
- Structure the Income Statement: Arrange these figures into a clear income statement format, starting with revenue, followed by expenses, and ending with net income.
Developing the Cash Flow Statement:
- Begin with Net Income: Start with the net income from your income statement.
- Adjust for Non-Cash Items: Add back non-cash expenses (like depreciation) that were deducted from net income but didn’t involve actual cash outflow.
- Analyze Cash Flow from Operations: Track the inflow and outflow of cash related to your core business activities.
- Track Investing and Financing Activities: Record cash flow from buying or selling assets, taking on debt, and receiving investments.
- Organize the Cash Flow Statement: Format this information into the standard three sections: operating, investing, and financing activities.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Even with the best intentions, there can be bumps in the road when preparing financial statements. Let’s tackle some common challenges:
1) Addressing Inconsistencies in Financial Data
Sometimes, numbers don’t add up. Maybe there’s a missing receipt or an invoice that was entered twice. In these cases, meticulous record-keeping is your best friend.
Tip: Regularly reconcile your bank statements with your internal records. This helps catch errors early and ensures your data is accurate.
2) Dealing with Cash vs. Accrual Accounting Methods:
Many small businesses use the cash accounting method, recording transactions when cash changes hands. However, the accrual method (recording transactions when they occur, regardless of cash flow) is often preferred for a more accurate financial picture.
Tip: If you need help determining which method is right for you, consult with an accountant. They can help you choose the method that aligns with your business goals and reporting needs.
How to Analyze Financial Health
Having accurate financial statements is just the first step. The real power comes from understanding what those numbers mean for your business. Financial analysis helps you interpret those figures and gain valuable insights into your overall financial health.
Key Financial Ratios and Metrics
Let’s explore some essential ratios and metrics that can help you assess your company’s financial performance:
1) Liquidity Ratios
- Current Ratio: This compares your current assets (cash, accounts receivable) to your current liabilities (accounts payable). A higher ratio indicates a greater ability to meet short-term obligations.
- Quick Ratio: Similar to the current ratio, but it excludes inventory (which may not be easily converted to cash). This provides a more conservative view of your liquidity.
2) Profitability Ratios
- Gross Profit Margin: This shows the percentage of revenue left after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). A higher margin indicates better profitability at the core business level.
- Net Profit Margin: This reveals the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after deducting all operating expenses, including operating costs, taxes, and interest. It’s a key indicator of overall profitability.
3) Efficiency Ratios
- Inventory Turnover: This measures how quickly you sell your inventory. A higher turnover rate generally means you’re managing inventory efficiently.
- Accounts Receivable Turnover: This calculates how quickly you collect payments from customers. A higher turnover rate indicates healthy cash flows from sales.
- Accounts Payable Turnover: This measures how quickly you pay your suppliers. A higher turnover rate means you’re managing your cash flow effectively.
Identify Financial Trends and Patterns
Analyzing your financial statements isn’t just about looking at the numbers in isolation. It’s about uncovering the story they tell about your business over time.
Don’t just look at your financial statements for a single month or quarter. Instead, compare them across multiple periods – month over month, quarter over quarter, or year over year. This allows you to:
- Spot Trends: Are your sales growing or declining? Are your expenses increasing at a faster rate than your revenue?
- Identify Seasonality: Does your business have busy seasons and slow seasons? Understanding these patterns can help you plan inventory, staffing, and marketing efforts.
- Track Progress: Are your profitability ratios improving? Are you becoming more efficient at managing your assets? Comparing statements over time helps you measure your progress and identify areas where you can continue to grow.
By carefully reviewing your financial statements, you can often uncover warning signs that might otherwise go unnoticed. For example, if your profit margins are shrinking, it could be a sign that your expenses are outpacing your revenue growth.
A rising debt-to-equity ratio might indicate that you rely too heavily on borrowing to finance your operations. If your inventory turnover rate is low, it could mean that you’re holding onto excess inventory, tying up valuable cash.
Once you’ve identified potential problems, you can take steps to address them. It may be time to cut costs, raise prices, or adjust your marketing strategy.
How to Leverage Financial Statements for Business Growth
Now that you’ve mastered the art of creating and analyzing financial statements, it’s time to unleash their full potential to fuel your business growth.
Make Informed Business Decisions
Financial statements aren’t just a historical record; they’re a powerful tool for strategic planning. By analyzing your financial data, you can identify trends, spot opportunities, and make informed decisions about where to invest your resources.
Whether it’s launching a new product line, expanding into new markets, or streamlining your operations, your financial statements provide the insights you need to make confident, data-driven decisions that align with your business goals.
Secure Funding and Investment
Whether you’re seeking a loan from a bank or pitching your business to potential investors, your financial statements are your most valuable asset. Lenders and investors carefully scrutinize these documents to assess your business’s financial health, profitability, and growth potential.
By presenting clear, accurate, and compelling financial statements, you demonstrate your credibility and increase your chances of securing the funding you need to take your business to the next level.
Final Thoughts on Small Business Financial Statements

So there you have it! We’ve covered the ins and outs of small business financial statements and why they are crucial to your success. From understanding your balance sheet to analyzing your cash flow statement, we’ve highlighted the importance of staying on top of these numbers.
But beyond just knowing how to read these statements, it’s essential to have a strong foundation in financial literacy. This includes having the knowledge to make informed decisions that can ultimately determine the future of your business.
As you wrap up this blog post, I urge you to review your financial statements. Are there any areas that need improvement? What changes can you make based on the information presented here?
Don’t let these statements gather dust in a folder somewhere—use them as a tool for ongoing financial analysis and decision-making. Your business’s success depends on it!
Keep pushing forward, stay financially savvy, and watch your business thrive!







